SKELETAL SYSTEM Comprising the axial skeleton (including the bones of the head, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum) and the appendicular skeleton (bones offline extremities).
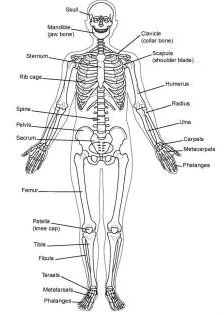
Table of Contents
1.SKELETAL SYSTEM(BONES,JOINTS)
I. BONES
Is not classified under connective tissue, this is a tissue of cells well referred to as osteocytes, which are situated in what is regarded as the ground substance. mixed with the tissue and collagen fibers in a structure that is comparatively stiff.
- Bones have a superficial thin layer of compact bone around a central mass of spongy bone, and internal soft tissue, the marrow, where blood progenitor cells are found.
Also store calcium and phosphorus in addition to functioning as the biomechanical levers on which muscles act and produce the movements in joints.
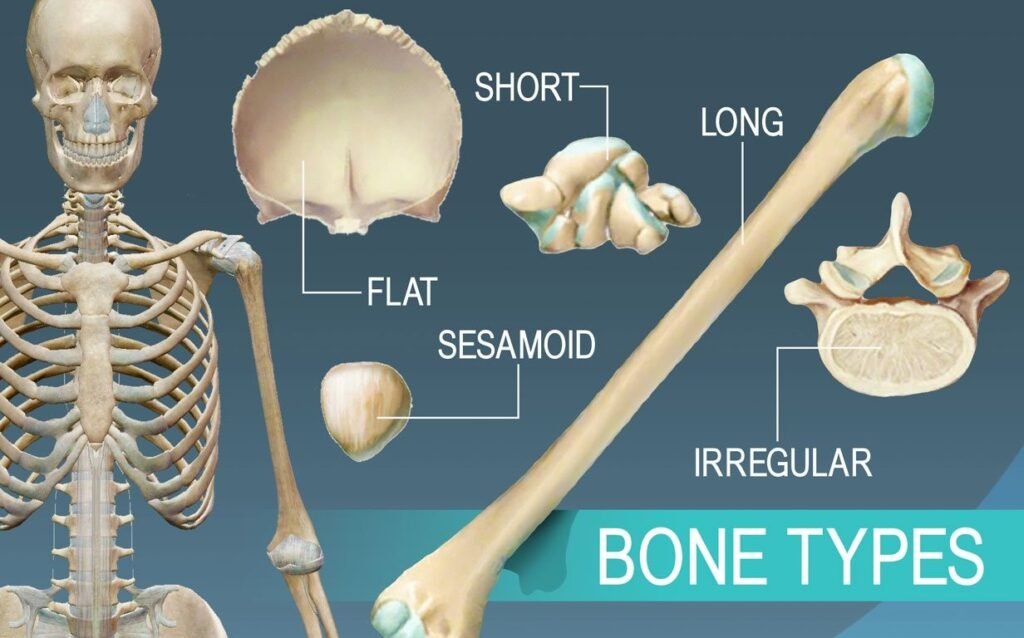
Are categorized of long bones, short bones, flat bones irregular bones and sesamoid bones
According to their developmental history, they are also categorized into endochondral and membranous bones.
A. Long bones 
Including the tibia, fibula, phalanges, humerus, radius, ulna, femur and metacarpals. Develop by replacement of hyaline cartilage plate (endochondral ossification).
Have a shaft (diaphysis) and two ends (epiphyses). metaphysis is part of the diaphysis adjacent to the epiphyses.
Diaphysis
The central part of the structure, known as the shaft, consists of a dense layer of compact bone. Encloses the marrow cavity.- Metaphysis
• It is the widened region of the diaphysis adjacent to the epiphysis. Growth plates are located between the metaphysis and epiphysis during bone development.
Epiphyses
• The broadened articular ends are divided from the shaft by the epiphyseal plate during development
bone growth and composed of a spongy bona surrounded by a thin layer of compact bona.
B. Short bones
• They include the carpal and tarsal bones and have a roughly cuboid shape
• They consist of spongy bone and marrow encased in a thin outer layer of compact bone.
- C. Flat Bones – ribs, sternum, scapulae, and cranial vault bones. Two layers of compact bone enclosing spongy bone with marrow space. Articular surfaces covered with fibrocartilage, grow by connective tissue replacement.
- D. Irregular Bones – bones of the face, vertebrae, and coccyx. Mostly spongy bone with thin outer layer of compact bone.
- E. Sesamoid Bones – develop in tendons, reduce friction, shift mechanical advantage, protect from wear. Commonly found where tendons cross synovial articulations in long bones of limbs (e.g. pisiform in wrist, patella in knee).
II. JOINTS
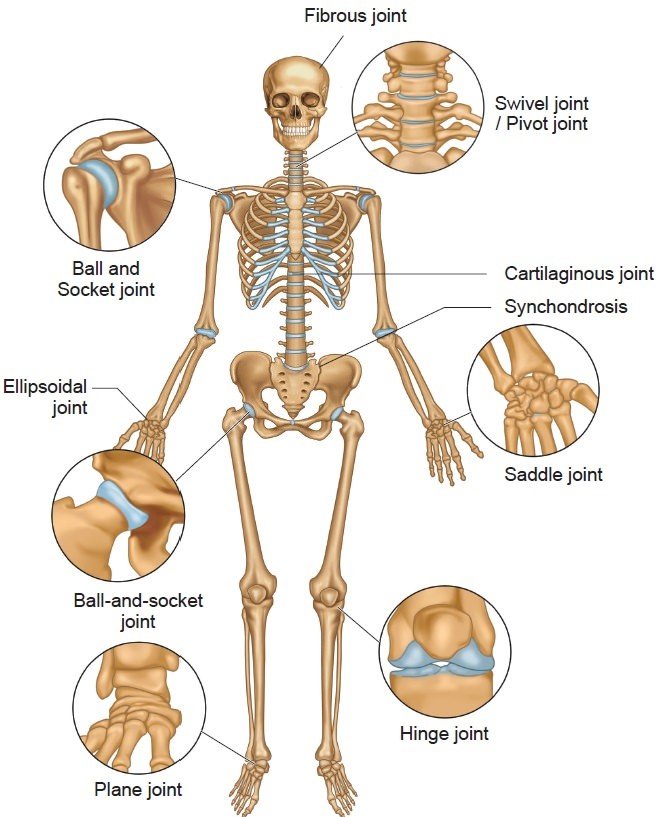
- IN SKELETAL SYSTEM Joints are the junctions where bones come together. They can be fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial. Fibrous joints have no joint cavities and allow little movement. Examples include sutures and syndesmosis. Cartilaginous joints are united by cartilage and also have no joint cavity. They can be primary, allowing little movement but permitting growth in childhood, or secondary, allowing slight movement. Synovial joints are found between separate skeletal elements and allow certain degrees of movement. They have a joint cavity, articular cartilage, synovial membrane, and articular capsule.
- They are junctions where two or more bones come together.
• They receive nerve supply such that the nerve serving a joint also innervates the muscles responsible for moving that joint and the skin covering the insertion of such muscles (Hillan law).
• They are categorized based on their structural characteristics into fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial types
A. Fibrous joints (synarthroses)
Are joined by fibrous tissue, have no joint cavities, and permit little movement.
1. Sutures
Are connected by fibrous connective tissue, such as the fibrous continuities between the flat bones of the skull.
2. Syndesmosis
Are connected by dense fibrous connective tissue. Occur as the inferior tibiofibular syndesmoses and tympanostapedial syndesmoses
between the footplate of the stapes and the oval window in the middle ear
B. Cartilaginous joints
Are united by cartilage and have no joint cavity.
1. Primary cartilaginous joints (synchondrosis)
Are united by hyaline cartilage and permit little to no movement but allow for growth in length during childhood and adolescence.
This includes epiphyseal cartilage plates (the connection between the epiphysis and the diaphysis in a growing bone) and spheno-occipital and manubriosternal synchondroses
2. Secondary cartilaginous joints (symphyses)
Are joined by fibrocartilage and are slightly movable joints.
Are all located in the median plane and include the pubic symphysis and the interver-tebral disks.
C. Synovial (diarthrodial) joints
Are found between two separate skeletal elements and permit certain degrees of movement
according to the shape of the articulation and/ or the type of movement.
They are defined by four structural features: joint cavity or space, articular (hyaline) cartilage
synovial membrane- that produces the synovial fluids, and articular capsule
- 1. Plane (gliding) joints
Have flat articular surfaces and allow a simple back-and-forth gliding or sliding of one
bone over the other. Occur in the proximal tibiofibular, intertarsal, intercarpal, intermetacarpal, carpometa carpal, sternoclavicular, and acromioclavicular joints.
2. Hinge (ginglymus) joints
Resemble door hinges and allow only flexion and extension.
These joints are found in the elbow, ankle, and interphalangeal joints.
3. Pivot (trochoid) joints
These joints are formed by a central bony pivot turning within a bony ring and permit only rotation. (movement around a single longitudinal axis).
Occur in the superior and inferior radio ulnar joints and in the atlantoaxial joint.
4. Condylar (ellipsoidal) joints
They feature two convex condyles articulating with two concave condyles. (The shape of the
articulation is ellipsoidal.)
Freely movable and are found in the wrist, the knuckle and the thumb. knee ( tibiofemoral), and atlanto-occipital joints.
5. Saddle (sellar) joints
Resemble the shape of a horse’s saddle and allow flexion/extension, abduction/adduction,
and circumduction, but no axial rotation.
These types of joints are found in the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb and between the femur and patella. - 6.Ball-and-socket (spheroidal or cotyloid joints )
Are done by the formation of a cup shaped cavity head and a receiving of a globular head into it. allow movement in many directions.
These joints permit flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, medial and lateral rotations, as well as circumduction, and are found in the shoulder and hip joints
Question: What are the two main divisions of the skeletal system? Answer: The skeletal system is divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
Question: What type of bone tissue is found around the central mass of spongy bone? Answer: Compact bone forms the superficial thin layer around the central mass of spongy bone in the skeletal system.
Question: Which bones are categorized as long bones in the skeletal system? Answer: Long bones in the skeletal system include the tibia, fibula, phalanges, humerus, radius, ulna, femur, and metacarpals.
Question: What are the structural features that define synovial joints in the skeletal system? Answer: Synovial joints in the skeletal system are defined by four structural features: a joint cavity or space, articular (hyaline) cartilage, a synovial membrane that produces synovial fluids, and an articular capsule.
Question: What type of joint is the elbow classified as in the skeletal system? Answer: The elbow is classified as a hinge (ginglymus) joint in the skeletal system.
Question: What is the role of sesamoid bones in the skeletal system? Answer: Sesamoid bones in the skeletal system develop in certain tendons to reduce friction on the tendon and shift the mechanical advantage, thus protecting it from excessive wear.
Question: Which type of bones consist of two layers of compact bone enclosing spongy bone with a marrow space? Answer: Flat bones in the skeletal system consist of two layers of compact bone enclosing spongy bone with a marrow space (diploe).
Question: How are primary cartilaginous joints, or synchondroses, characterized in the skeletal system? Answer: Primary cartilaginous joints, or synchondroses, in the skeletal system are united by hyaline cartilage and permit little to no movement but allow for growth in length during childhood and adolescence.
Question: What are the structural characteristics of plane (gliding) joints in the skeletal system? Answer: Plane (gliding) joints in the skeletal system have flat articular surfaces and allow a simple back-and-forth gliding or sliding of one bone over the other.
Question: What bones are included in the category of irregular bones in the skeletal system? Answer: Irregular bones in the skeletal system include bones of mixed shapes, such as bones of the face, vertebrae, and some others.
Question: What type of bones are the carpal and tarsal bones, and what is their shape and composition? Answer: The carpal and tarsal bones are categorized as short bones. They have a roughly cuboid shape and consist of spongy bone and marrow encased in a thin outer layer of compact bone.
Question: How are flat bones structurally composed, and can you provide examples of such bones? Answer: Flat bones consist of two layers of compact bone enclosing spongy bone with a marrow space (diploe). Examples of flat bones include the ribs, sternum, scapulae, and bones of the cranial vault.
Question: What is the composition and function of sesamoid bones, and where are they commonly found? Answer: Sesamoid bones develop in certain tendons to reduce friction on the tendon and shift the mechanical advantage, protecting it from excessive wear. They are commonly found where tendons cross synovial articulations at the ends of long bones, such as the pisiform in the wrist and the patella in the knee.
Question: What are the characteristics of primary cartilaginous joints, and where can they be found? Answer: Primary cartilaginous joints, or synchondroses, are united by hyaline cartilage and permit little to no movement but allow for growth in length during childhood and adolescence. They include epiphyseal cartilage plates, spheno-occipital, and manubriosternal synchondroses.
Question: Describe the structural features and movement capabilities of ball-and-socket joints. Answer: Ball-and-socket joints are formed by a cup-shaped cavity receiving a globular head, allowing movement in many directions. These joints permit flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, medial and lateral rotations, as well as circumduction. They are found in the shoulder and hip joints.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21048-skeletal-system

This was a very good post. Check out my web page Webemail24 for additional views concerning about Website Design.
Thank you so much for your kind words! I’m glad you enjoyed the post. I’ll definitely check out your webpage, Webemail24, for more insights on website design. I appreciate the recommendation!