Learn about the key functions and structures of the human body digestive, respiratory, urinary, reproductive, endocrine and integumentary organ systems. Learn how these systems work together to maintain health, enable growth, and permit reproduction.
Table of Contents
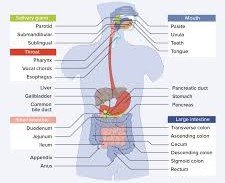
I. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
- In organ system it consists of three main divisions of the visceral tube, which are the mouth, the pharynx, and the alimentary canal. The alimentary canal itself encompasses the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Each part contributes differently to the process involved in food digestion, nutrient absorption, and waste product excretion from the body.
- Also contains accessory organs and glands to aid in digestion and nutrient storage, including the salivary glands, liver, gall bladder, and pancreas.
- Performs specific functions: essential food-processing activities. In the mouth, the food is moistened by saliva; is masticated and mixed by the mandible, teeth, and tongue; and is propelled by the pharynx and esophagus into the stomach, where it is mixed with the gastric juice and converted into chyme.
- Performs specific functions: in the small intestine, the food or chyme is digested by secretions from glands in the intestinal wall and from the liver; gallbladder, and pancreas; and digested end products are absorbed into the blood and lymph capillaries in the intestinal wall.
- Performs specific functions: in the large intestine, water and electrolytes are absorbed, and the waste products are transported to the rectum and anal canal, where they are eliminated as feces.
- Liver stores and releases glucose, breaks down toxins, and marshals cholesterol metabolism.
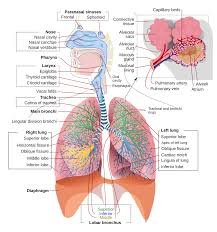
II. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
- Consists of a conducting portion that transports filtered, humidified, and warmed air to the lungs. Includes the nose/nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi.
- Consists of a respiratory portion in the lungs, which contain the terminal air sacs, or alveoli, where gas exchange occurs; oxygen in the air is exchanged for carbon dioxide in the blood.
- Air movements at rest are aided by the diaphragm and thoracic cage.
- The respiratory system plays a role in the production of speech through periodic expulsion of air along with the opening and closure of the glottis, which helps in the production of sound to articulate speech..
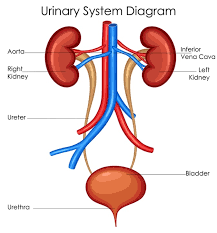
Ill. URINARY SYSTEM
- In organ system Kidneys produce urine and are important in maintaining water and electrolyte balance, acid-base balance, regulating urine volume and composition, regulating blood volume, and in eliminating waste products from the blood. Also, through structures in the kidney, stimulates red blood cell production and helps in the control of blood pressure.
- The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder, where the urine is held until it leaves the body.
- Bladder stores urine and drains through the urethra out of the body.
IV. REPRODUCTIVE ORGAN SYSTEM
Male reproductive organ system:
- Includes testes that produce spermatozoa and androgenic hormones.
- Has ducts (epididymis, ductus deferens, and ejaculatory ducts) that transmit spermatozoa from the testis to the prostatic urethra.
- Glands, such as the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands, contribute secretions to the seminal fluid as it passes through the urethra.
- The urethra passes the ejaculate to an opening at the tip of the external genital organ, the penis.
Female reproductive organ system system
- Consists of Organ system that include ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, and external genital organs. The ovaries produce steroid hormones and also oocytes (ova or eggs) that are conveyed from the ovaries through the uterine tubes to the cavity of the uterus. Each ovulated oocyte is released into the peritoneal cavity of the pelvis; one of the uterine tubes captures the oocyte, where it begins its journey toward the uterus. The uterine tubas transmit spermatozoa in the opposite direction, and fertilization of an oocyte usually occurs within the expanded ampulla of a uterine tube. A fertilized oocyte becomes embedded in the wall of the uterus, where it develops and grows into a fetus, which passes through the uterus and vagina (together called the birth canal). The vagina provides a passage for delivery of an infant; it also receives the penis and semen during sexual intercourse.
- Includes female external genitalia: the mons pubis, which is a fatty eminence anterior to the symphysis pubis; the labia majora, which are two large folds of the skin; the labia minora, which are two smaller skin folds that commence at the glans clitoris, lack hair, and contain no fat; the vestibule, which is an entrance of the vagina between the two labia minora; has the hymen at the vaginal orifice; and the clitoris ( crura, body, and glans or head), which is composed largely of erectile tissue and is hooded by the prepuce of the clitoris.
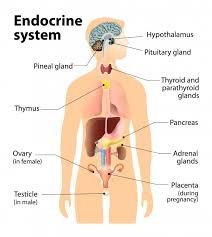
V. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- Ductless endocrine glands secrete hormones, or messenger molecules, directly into the blood circulation and are carried to body cells.
- The endocrine system controls and integrates many other organ systems in the body, thus having a major impact on the process of reproduction, growth, and metabolism. It works to maintain homeostasis and control responses to both internal and external stimuli through its release of hormones..
- Functions tend to be slower processes compared to those controlled by the nervous system.
- Pure endocrine organs include the pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, and suprarenal glands.
- Other endocrine cells are contained in the pancreas, thymus, gonads, hypothalamus, kidneys, liver, stomach, and the walls of the intestine.
- Tropic hormones are hormones that regulate the functions of other endocrine glands.
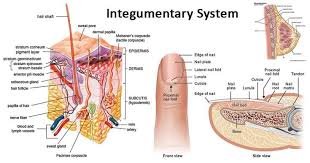
VI. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
- Includes skin (integument) and its appendages, including sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair, and nails.
- Contains sensory receptors associated with nerve endings for pain, temperature, touch, and pressure.
- Represents the largest single organ in the body.
Skin
- Consists of the avascular epidermis as the superficial, or surfacing, layer of stratified squamous epithelium that develops from ectoderm and has a keratinized layer on the outside of the body; it ls thickest on the palms and the soles.
- The dermis is a deeper layer of connective tissue that develops largely from the mesoderm and contains down growths from the epidermis, such as hair follicles and glands.
- The hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) is a fatty layer that lies deep in the dermis and is part of the superficial fascia. This layer is highly vascular and can serve as a route to administer medications via injection.
- The skin is a protective layer. an extensive sensory organ and is significant in body temperature regulation, fluid balance, production of vitamin D, and at least some absorption.
Appendages of the skin
- Sweat glands develop as epidermal downgrowth, have excretory functions, and regulate body temperature and fluid balance.
- Sebaceous glands develop from the epidermis (as down growths from hair follicles into the dermis) that empties their oily sebum into hair follicles to provide a lubricant to the hair and skin and protect the skin from drying.
- Hairs develop as epidermal down growths and function in protection, regulation of body temperature, and facilitate evaporation of perspiration.
- Nails develop as epidermal thickenings to protect the sensitive tips of the digits and function in delicate manipulations.
Q/A
1. What is the Digestive System(organ system), and How Does It Work?
The digestive process is done by the digestive system, where food is digested and changed into nutrients for use by the body in energy, growth, and repair. It consists of three main parts: the mouth, the pharynx, and the alimentary canal, which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Accessory organs that contribute an important part to digestion and nutrient storage include salivary glands, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Mouth and Pharynx: Food enters this part where food is moistened, chewed, and mixed with saliva to begin the digestion process of the body
Stomach: Food mixed with the gastric juices forming chyme
Small Intestine: Chyme digested, nutrients absorbed
Large Intestine: Water and electrolytes absorbed, the waste expelled as feces
2. What is Respiratory System(Organ system)?
The respiratory system is responsible for respiration and the exchange of gases. It includes the conducting portion, which consists of the nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi, while the respiratory portion consists of lungs and alveoli.
Conducting part: Filtering, humidifying, and warming of air before entering the lungs.
Respiratory part: The process of exchange of gases, which is the exchange of oxygen from the inhaled air with carbon dioxide through the blood stream, takes place in the alveoli.
Speech Production: The respiratory system allows the process of speech production through the control of the flow of air across the vocal folds.
3. What is the Function of Urinary System(Organ system)?
The urinary system is responsible in the maintenance of internal environment by managing the normal level of body water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance. Organs of this system are kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Kidneys: Kidneys produce urine, modify the content of blood volume, filter blood waste, and regulate electrolytes.
Ureters: Transport urine from the kidney to the bladder.
Bladder: Stores urine until it leaves the body via the urethra.
4. What Are the Main Functions of the Reproductive System(Organ system)?
The reproductive system is capable of producing children and passing on genes. It differs between male and female:
Male Reproductive System: It includes testes, which manufacture sperm and a hormone; ducts-including epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts-transport sperm out of the body, and glands-seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands-which add secretions to sperm. Sperm moves through and is ejaculated from the urethra.
Female Reproductive System: It includes Organ system of ovaries that produce eggs and a hormone; uterine tubes where fertilization takes place; the uterus, where an embryo develops; the vagina; and external genital organs.
5. How does the endocrine system regulate the functions of the body?
The endocrine system is made up of ductless glands that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system regulates a wide range of physiological activities, such as growth and metabolism, and reproductive processes.
Glands: Include the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and others that produce specific hormones.
Hormones: Chemical messengers whose function is to affect metabolism, immune responses, and mood.
Homeostasis: Maintains the body’s internal environment by reacting to changes within and outside the body.
6. What is the purpose of the integumentary system(Organ system)?
The integumentary system includes skin, hair, nails, and related glands. It acts as a first line of defense that provides a protective barrier between the internal tissues and the external environment as it carries out the following functions:
Protection: It protects the internal tissues from physical injury, disease organisms, and water loss.
Sensory Function: It contains receptors for pain, temperature, and touch.
Regulation: It helps regulate body temperature by releasing sweat and varying blood flow through the body.
7. How do these organ systems work together to keep a person healthy?
All the organ systems interrelate with each other to maintain in the body homeostasis, which aids in growth and survival.
Regulation: Nervous system and endocrine system coordinate the activities of all organ systems
Protection and locomotion: Muscular and skeletal systems enable locomotion, which depends on oxygen and nutrients supplied by the respiratory and digestive systems.
Reproduction: The system works in close coordination with the endocrine system for regulating the sexual maturation processes along with reproduction.
Excretion: The waste products are excreted by the urinary and digestive systems so that toxicity can be avoided.
