Explore the complexities of the nervous system, covering its anatomical divisions into the central and peripheral nervous systems, and functional divisions into the somatic and autonomic systems. Learn about neuron structures, classifications, and roles in brain and spinal cord functions, and how the autonomic system regulates involuntary bodily functions. Ideal for students and professionals interested in neuroscience
Table of Contents
1.NERVOUS SYSTEM
The nervous system is split into two main parts based on anatomy: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), made up of 12 cranial nerve pairs and 31 spinal nerve pairs, along with their related ganglia
Is divided functionally into the somatic nervous system, which controls primarily voluntary activities, and the visceral (autonomic) nervous system, which controls primarily involuntary activities.
Is composed of neurons and neuroglia (non-neuronal cells such as astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia} and controls and integrates the body activity.
2.NEURONS
- Are the structural and functional units of the nervous system (neuron doctrine).
- Are specialized in the reception, integration, transformation, and transmission of information.
A. Components of neurons:
- Collections of neuronal cell bod in are termed gray matter ornuclei in the CNS. and collections of neuronal cell bodies are called ganglia in the PNS.
- Dendrites (dendron means “tree”) are highly branched extensions from the cell body that carry impulses from local circuitry toward the cell body.
- Axons tend to be long and usually come in single strands, with just a few offshoots called collaterals. Their main job is to send electrical impulses away from the cell body of the neuron
B. Classification of neurons based on shape:
1.Unipolar (pseudo unipolar) neurons:
- Have one process, which divides into a branch directed at the CNS and a peripheral branch that brings information toward the cell body from peripheral receptors.
- Are called pseudo unipolar because they were originally bipolar, but their two processes fuse during development to form a single process that bifurcates at a distance from the cell body.
- Are sensory neurons of the PNS and found in spinal and cranial nerve ganglia.
2.Bipolar neurons:
- Have two proce11H one proximal (CNS) and the other Is distal (PNS).
- These are associated with specialized senses such as smell, sight, and hearing.
3.Multipolar neurons:
Have several dendrites and one axon and are most common in the CNS (e.g., motor cells in the anterior and lateral horns of the spinal cord, autonomic ganglion cells).
C. Clusters of nerve call bodies:
- A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies outside the CNS {e.g., dorsal root ganglion, autonomic ganglia).
- A collection of neuron cell bodies within the CNS is called a nucleus. An exception is the basal ganglia, which is a group of subcortical nuclei.
D. Other components of the nervous tissues/system:
1.Cells that support neurons:
- Include Schwann cells and satellite cells in the PNS.
- Are called neuroglia in the CNS and are composed mainly of three types: astrocytes; oligodendrocy181, which plays a role in myelin formation and transport of material to neurons; and microglia, which phagocytose waste products of nerve tissue.
2.Myalin:
- Is the membrane-wrapped sheath around certain nerve axons.
- Schwann cells in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and oligodendrocytes in the Central Nervous System (CNS) create this structure.
3. Synapses:
- Are the sites of functional contact of an axon terminal of one neuron with the cell body or dendrites of another neuron, or an effector (muscle and gland) cell, or a sensory receptor cell.
- Are classified by the site of contact as axodendritic, axoaxonic, or axosomatic.
- Are the sites of impulse transmission commonly from the axon terminals (presynaptic elements) to the plasma membranes (postsynaptic elements) of the receiving cell via a neural transmitter across the synaptic cleft.
3. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM:
1.Brain
- Is enclosed within the cranlal vault.
- Has a cortex, which is the outer part of the cerebral hemispheres, composed of gray matter. This matter consists largely of the nerve call bodies, dendrites, and neuroglla.
- Has an interior part composed of white matter, which consists largely of axons forming tracts or pathways, and ventricles, which are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSP).
2.Spinal cord
- It has a cylindrical shape, fills about two-thirds of the upper vertebral canal, and is wrapped in the protective layers of the meninges.
- It features enlargements in the cervical and lumbar regions that provide nerve connections to the upper and lower limbs, respectively.
- Has centrally located gray matter and peripherally located white matter.
- The spinal cord is shorter than the vertebral canal, ending between L1 and L2 vertebral level because the cord grows more slowly than the surrounding vertebral column during fetal development.
- The tapered end of the spinal cord, known as the conus medullaris, is situated around the L2 vertebra in adults, and at L3 in newborns
- The conus medullaris attaches caudally to the coccyx through the sacral canal via the filum terminale located among the roots of the cauda equina.
3.Meninges
- Consist of three layers of connective tissue membranes (pia, arachnoid, and dun mater) that surround and protect the brain and the spinal cord.
- Contains the subarachnoid space, which is the interval between the arachnoid and pia mater, filled with CSR.
- The pia mater carries the vascular supply to the surface of the brain and spinal cord and is intimately invested with the external surfaces of these.
4.Cerebrospinal fluid
- Is produced by vascular choroid plexuses in the lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle of the brain.
- Flows through the ventricles to drain into the subarachnoid space from the fourth ventricle.
4. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
A. Cranial nerves
- Consist of 12 pairs and are connected to the brain and brainstem.
- Motor fibers have their cell bodies inside the central nervous system (CNS), while sensory fibers originate from cell bodies that form sensory ganglia outside the CNS.
- Emerge from the ventral aspect of the brain (except for the trochlear nerve, or cranial nerve IV).
- Contain different functional components based on the cranial nerve functions.
B. Spinal nerves
- There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, divided into 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal.
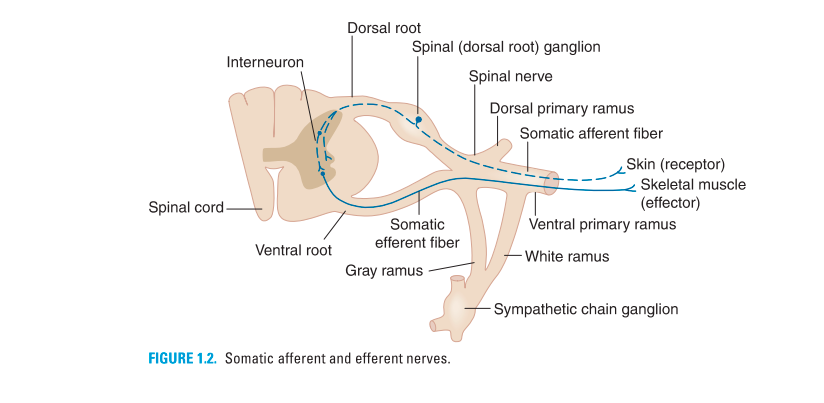
- Are formed from dorsal and ventral roots; each dorsal root has a ganglion that is associated with each intervertebral foramen.
- Are connected with the sympathetic chain ganglia by white (T1-L2) and gray (all spinal nerves) rami (communicantes).
- Contain sensory fibers with cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion for somatic and visceral sensations.
- Contain motor fibers with cell bodies in the anterior horn of all levels of the spinal cord for stimulation of skeletal muscles and visceral motor fibers from cell bodies in the lateral horn of the spinal cord (T1 through L2, S2, S3, and S4).
- Branch into ventral primary rami to supply for the body wall through major plexuses (i.e., cervical, brachial, and lumbosacral) and intercostal nerves.
- Branch into the dorsal primary rami to innervate the skin and deep muscles of the back.
C. Functional components in peripheral nerves
1.Somatic afferent fibers (formerly general somatic afferent)
Transmit pain, temperature, touch, and proprioception from peripheral receptors or the skin of the body to the CNS.
2.Somatic efferent fibers (formerly general somatic efferent
Carry motor impulses from CNS motoneurons to the skeletal muscles of the body.
3.Visceral afferent fibers (formerly general visceral afferent)
Convey sensory impulses from visceral organs and blood vessels to the CNS.
4.Visceral efferent fibers (autonomic nerves, formerly general visceral efferent)
Transmit motor impulses from the CNS through a peripheral autonomic ganglion to smooth muscle of the viscera or blood vessels, cardiac muscle, and glandular tissues.
5.Special sensory fibers (formerly special somatic afferent and special visceral afferent)
- Convey special sensory impulses of the eye and ear for vision, hearing, and equilibration through cranial nerves to the CNS.
- Transmit senses of smell from the nasal cavity and taste sensations from the oral cavity through cranial nerves to the CNS.


6.Special visceral efferent fibers (old terminology)
- Conduct motor impulses to the muscles that develop in association with one of the branchiomeric arches: first arch-muscles for mastication; second arch-muscles for facial expression; third arch-stylopharyngeus muscle; fourth arch-palatal and pharyngeal muscles for elevation of the pharynx; or sixth arch-movement of the larynx
- There is no fifth arch.
- This scheme ls not used as widely as it was previously and will not show up on board examinations.
5. AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Is responsible for the motor innervation of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
It is divided into the sympathetic (thoracolumbar outflow), parasympathetic (craniosacral outflow), and enteric divisions.
Is composed of two neurons, preganglionic and postganglionic, which are visceral efferent neurons. It has cholinergic fibers (sympathetic preganglionic, parasympathetic preganglionic and parasympathetic postganglionic) and adrenergic fibers (sympathetic postganglionic) except those sweat glands (cholinergic).
Preganglionic neuron cell bodies are in the CNS, whereas postganglionic neuron cell bodies are in ganglia in the PNS.
1.Sympathetic nerve fibers (see Figure 1.3)
- Have preganglionic nerve cell bodies that are located in the lateral horn of the thoracic and upper lumbar levels (12 or L1-L3) of the spinal cord.
- Have preganglionic fibers that pass out of the spinal cord through ventral roots, spinal nerves, and then enter the white rami (communicantes).
- Preganglionic fibers enter adjacent sympathetic chain ganglia, where they synapse or travel up or down the chain to synapse in remote chain ganglia for the autonomics of the body wall.
- Postganglionic fibers from the neurons in the chain ganglia return to spinal nerves byway of gray rami and supply the skin with secretory fibers to sweat glands, motor fibers to smooth muscles of the hair follicles (arrectores pilorum), and vasomotor fibers to the blood vessels of the body wall.
- Alternatively, preganglionic fibers run ventrally through to the splanchnic nerves to synapse in preaortic (collateral) ganglia.
- Postganglionic fibers from the preaortic ganglia travel with arteries to innervate the viscera of the abdomen and pelvis.
- Sympathetic functions primarily in emergencies or catabolism (energy consumption), preparing individuals for fight or flight, and thus increase the heart rate, inhibit GI motility and secretion, and dilate pupils and bronchial lumen.
- They release norepinephrine (with the exception of sweat glands) and are categorized as adrenergic.
2.Parasympathetic nerve fibers
- Comprise the preganglionic fibers that arise from the brainstem (cranial nerves III, VII, IX, and X) and the second, third, and fourth sacral spinal segments.
- Are distributed to the internal organs and walls of the viscera and glands of the digestive and respiratory systems but not to the skin or body wall and limbs.
- Decrease the heart rate, increase GI peristalsis, and stimulate secretory activity.
Functions:
- Parasympathetics function primarily in homeostasis or anabolism (energy conservation), tending to promote quiet and orderly processes of the body.
- They liberate acetylcholine and are classified as cholinergic.
3.Enteric division
- Consists of a complex web of interconnecting neurons with multiple different neurotransmitters located in the walls of the GI tract.
- The enteric ganglia are parasympathetic postganglionic neuron cell bodies and plexuses of the GI tract that include the classically described myenteric (Auerbach)and submucosal (Meissner)plexuses.
- It significantly influences the regulation of gastrointestinal motility and secretion.
.
Q/A
What are the two primary anatomical divisions of the nervous system?
- The nervous system is primarily split into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, whereas the PNS is composed of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves, each accompanied by its associated ganglia.
How is the nervous system categorized based on its function?
- From a functional perspective, the nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system, which mainly manages voluntary actions, and the autonomic (visceral) nervous system, which regulates involuntary actions.
Can you describe neurons and their function within the nervous system?
- Neurons are fundamental building blocks of the nervous system, tasked with receiving, processing, and transmitting information. These actions are vital for the coordination and regulation of bodily functions.
What are the key components of neurons in the nervous system?
- Neurons consist of dendrites, which are tree-like branches that receive signals, and axons, long fibers that transmit signals away from the neuron. Groups of these neurons form nuclei in the CNS and ganglia in the PNS.
What types of cells provide support to neurons in the nervous system?
- In the nervous system, neurons are supported by neuroglia in the CNS, which includes cells like astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia, and by Schwann cells and satellite cells in the PNS. These cells assist in tasks from myelin sheath formation to waste removal.
What role does myelin play within the nervous system?
- Myelin, a protective sheath surrounding nerve axons, is crucial for insulating these fibers and speeding up electrical impulses. It is produced by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS.
How are synapses classified within the nervous system?
- Synapses in the nervous system are categorized by their connection points: axodendritic (between an axon and a dendrite), axoaxonic (between two axons), and axosomatic (between an axon and a neuron’s body).
What is the importance of the autonomic division in the nervous system?
- The autonomic division, encompassing the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, is essential for managing involuntary bodily functions like heartbeat and digestion, ensuring the body maintains equilibrium and responds effectively to stress.
What is the function of the enteric division in the nervous system?
- The enteric division operates independently within the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, controlling digestion and gastrointestinal motility through its intricate network of neurons, showcasing the nervous system’s intricate autonomy.
How do cranial nerves operate within the peripheral nervous system?
- Cranial nerves, which number 12 pairs, link directly to the brain and brainstem, carrying motor and sensory signals via neurons housed within the CNS and in peripheral sensory ganglia, thereby facilitating complex sensory and motor functions.
What function does the spinal cord serve in the central nervous system?
- Serving as a major communication route between the brain and body, the spinal cord processes reflexes and motor and sensory information within the central nervous system, residing within the vertebral column.
Describe the function of the meninges within the nervous system.
- The meninges, comprising three protective layers around the brain and spinal cord, act as a shield against infection and physical damage while containing and circulating cerebrospinal fluid, essential for nutrient transport and waste removal.
How does cerebrospinal fluid support the nervous system?
- Cerebrospinal fluid cushions the brain and spinal cord while facilitating the transport of essential nutrients and biochemicals necessary for the nervous system’s function and health.
What are the primary functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
- The sympathetic nervous system gears the body for action (fight-or-flight), increasing heart rate and energy expenditure, whereas the parasympathetic system promotes rest and digestion, conserving energy and enhancing metabolic processes.
What unique roles do special sensory fibers play in the nervous system?
- Special sensory fibers handle specific sensory inputs such as sight, hearing, taste, and smell, transmitting this information from sensory organs directly to the brain, facilitating our interaction with the environment through detailed sensory perception.
